Unplugging a peripheral component such as a "mouse" from a personal computer renders all of the software programs that require that component unusable on that computer. ██ ██████ ████████ █████████ █ ████████ ███████ ████ ████████ █ █████ ███ ██████ █████████ ██ ██ ████ ██ ████ ███ █████ ███ ██████ ████████ ██████ ██████████
The author concludes that Fred’s computer mouse must have been unplugged. He supports this by saying that unplugging the mouse from a computer causes all programs that require the mouse to become unusable. He then notes that a software program on Fred’s computer that requires the mouse has become unusable.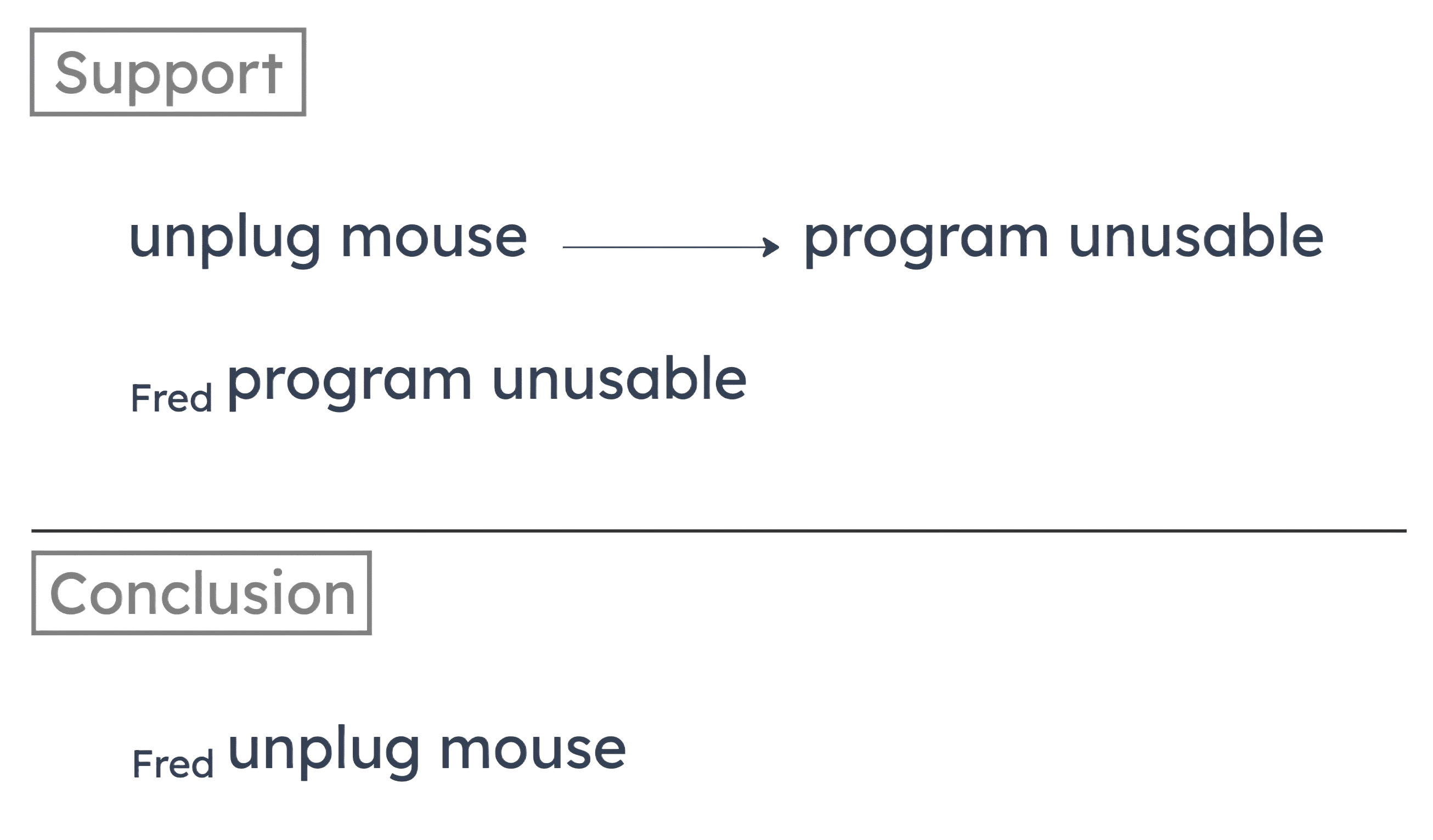
This is the flaw of mistaking sufficiency for necessity. The author treats “unplugging the mouse” as necessary for “the program becoming unusable.” But according to his argument, “unplugging the mouse” is sufficient, not necessary.
In other words, the argument overlooks the possibility that Fred’s program could become unusable without his mouse becoming unplugged.
The argument is most vulnerable ██ █████ ███ ██ ███ █████████ ███████████
It contains a █████ ██ ███ ███████ ██ ██████████ ████ ████████████ █████████ ██ ████████████ ██████████
It treats an █████ ████ ███ █████ █ ███████ ██████ ██ ██████ ████ █████ ██ █████████ ██ █████ █████ ████ ███████
It introduces information █████████ ██ ███ ██████████ ██ ████████ ██ ███████ ██ ████ ███████████
It attempts to ███████ ███ ██████████ ██ ██████ █ ██████████████ ████ ██ ███ ██████
It overlooks the ███████████ ████ ████ ████████ ██ ███ ███████ █ ██████████ █████████ ████ ██ █ ██████
